From MIT Dropout to AI Billionaire: How Alexandr Wang and Scale AI Reshape the Global AI Landscape
In the pantheon of Silicon Valley legends, few stories capture the audacious spirit of technological revolution as vividly as that of Alexandr Wang. At 28, this Los Alamos-born prodigy has orchestrated what may be the most consequential business transformation in artificial intelligence history a $14.3 billion Meta investment that not only reshaped his company’s destiny but potentially altered the trajectory of the global race for artificial superintelligence. Wang’s journey from MIT dropout to the architect of AI’s data infrastructure empire represents more than entrepreneurial success; it embodies the profound shift in how artificial intelligence systems are conceived, built, and deployed at unprecedented scale.
The magnitude of Wang’s achievement becomes clear when examining the numbers: Scale AI’s revenue explosion from $30 million in 2019 to a projected $2 billion in 2025, accompanied by a valuation surge from unicorn status to $29 billion in just six years. Yet behind these staggering figures lies a more compelling narrative about the invisible human infrastructure powering the AI revolution a story that encompasses triumph, controversy, and the complex ethical considerations that define our technological future.
Who Is Alexandr Wang? The Making of an AI Visionary
Born in January 1997 in Los Alamos, New Mexico, to Chinese immigrant parents who worked as nuclear physicists at the Los Alamos National Laboratory, Wang was immersed in scientific rigor from his earliest years. His parents’ classified work on nuclear weapons research would prove prophetic, as Wang would later secure multi-million-dollar defense contracts for his own company. The dinner table conversations in his household centered around “black holes and wormholes and alien life and supernova and far away galaxies,” creating an environment where ambitious thinking and rigorous problem-solving were fundamental values.
Wang’s intellectual prowess manifested remarkably early. His parents taught him algebra in second grade, and by fourth grade, he could perform basic geometry. “By the time I was in middle school I was doing calculus,” Wang recalled, adding that he scored “the best out of any fourth grader in New Mexico” in his first math competition, which “activated this competitive gene” that would drive his future success. This mathematical foundation led to national recognition through his qualification for the Math Olympiad Program in 2013, the US Physics Team in 2014, and USACO finalist positions in both 2012 and 2013.
The trajectory that would lead Wang to AI dominance began during his teenage years as a software programmer at Quora. Working 12-hour days during his gap year, Wang witnessed firsthand how even sophisticated tech companies struggled with data quality and annotation challenges. This experience planted the seeds for what would become Scale AI’s core value proposition: transforming raw, chaotic data into the precisely labeled datasets that AI systems require to function effectively.
Wang’s decision to drop out of MIT after his freshman year in 2016 wasn’t academic failure it was strategic opportunism. “I remember thinking, if the future is happening now, why not build it instead of waiting four years for a diploma?” he reflected. Driven by the conviction that labeled data, not just smarter algorithms, would power true AI advancement, Wang made the calculated decision to pursue his vision immediately rather than defer it for traditional credentials.
The Birth of Scale AI: A Startup Story Built on Prescient Vision
In the summer of 2016, Wang joined Y Combinator’s prestigious S16 batch alongside co-founder Lucy Guo, another Quora alumnus. Their initial pitch—an “API for human labor”—seemed almost mundane compared to the flashier startups in their cohort. While other companies pursued consumer applications or enterprise software, Wang and Guo were building what many investors initially dismissed as a sophisticated version of Amazon Mechanical Turk.
Yet Wang possessed a prescient understanding of artificial intelligence’s trajectory that would prove transformative. He recognized that the bottleneck for AI advancement wouldn’t be computational power or algorithmic innovation, but rather the availability of high-quality, precisely labeled training data. “Data is the new code,” Wang told Forbes in 2019, articulating a vision that seemed esoteric then but appears prophetic today.
The Y Combinator experience proved crucial in validating Wang’s thesis. Partner Jared Friedman noted that Scale was “taking advantage of an opportunity that is hiding in plain sight”. The company’s early traction came from autonomous vehicle startups desperate for labeled lidar and camera data a market that would explode as billions flowed into self-driving car development.
Lucy Guo’s departure in 2018 marked a pivotal moment in Scale’s evolution. Reports indicate she was removed due to “differences in product vision and road map,” though the exact circumstances remained controversial. Her exit consolidated Wang’s control over the company’s strategic direction and allowed him to pursue his ambitious vision of building AI’s data infrastructure without internal conflicts.
By 2019, Scale AI achieved unicorn status with a $100 million investment from Peter Thiel’s Founders Fund, valuing the company at $1 billion. This milestone made Wang, at 24, briefly the world’s youngest self-made billionaire a title that would fluctuate with market conditions but ultimately be secured by the 2025 Meta deal.
What Is Scale AI and How Does It Work? The Data Factory Revolution
Scale AI operates what can best be described as a “data factory for artificial intelligence” a sophisticated platform that transforms raw, unlabeled information into the precisely annotated datasets that power modern AI systems. The company’s operations span three primary platforms, each addressing different aspects of AI development:
Remotasks serves as Scale’s primary computer vision and autonomous vehicle data labeling platform. Through this system, contractors worldwide—primarily in the Philippines, Kenya, Venezuela, and other developing nations—perform intricate annotation tasks. These workers identify objects in images, draw bounding boxes around vehicles and pedestrians, and create the semantic segmentation maps that teach self-driving cars to navigate complex environments.
Outlier focuses on large language model (LLM) improvement through reinforcement learning with human feedback (RLHF). This platform employs specialized contractors to rate AI responses, correct model outputs, and provide the nuanced feedback that transforms raw language models into helpful, harmless, and honest AI assistants. The platform has been instrumental in improving models from OpenAI, Anthropic, and other leading AI companies.
The Safety, Evaluation and Alignment Lab (SEAL) represents Scale’s most sophisticated offering, focusing on red-teaming and evaluating frontier AI models. This division works directly with AI companies and government agencies to identify potential risks, biases, and failure modes in advanced AI systems before deployment.
The Human Infrastructure Behind AI
Scale’s competitive advantage lies not just in technology but in its sophisticated management of human intelligence at scale. The company employs a multi-tiered quality control system that combines automated pre-labeling, expert human reviewers, and machine learning algorithms to detect annotation errors. This hybrid approach achieves accuracy rates exceeding 99.9% while maintaining cost efficiency that traditional annotation services cannot match.
The company’s “expert marketplace” represents a particularly innovative aspect of its operations. Scale maintains a curated network of subject matter experts from PhD-level scientists to specialized domain experts who handle the most complex annotation tasks. Individual annotations in this tier can cost up to $100, reflecting the specialized knowledge required for tasks like medical imaging annotation or scientific document analysis.
Data Network Effects: Scale’s Defensive Moat
Wang’s strategic insight into data network effects has proven central to Scale’s durability as a business. Each new client brings unique edge cases and annotation challenges that strengthen Scale’s overall capabilities. When Toyota requires lidar data for Japanese driving conditions, or when the Pentagon needs satellite imagery analysis, these specialized requirements expand Scale’s knowledge base and improve its service quality for all clients.
This dynamic creates a virtuous cycle: better service quality attracts more prestigious clients, which generates more complex data challenges, which further improves Scale’s capabilities. The result is a defensive moat that becomes stronger with scale—exactly the type of business model that justifies premium valuations in competitive markets.
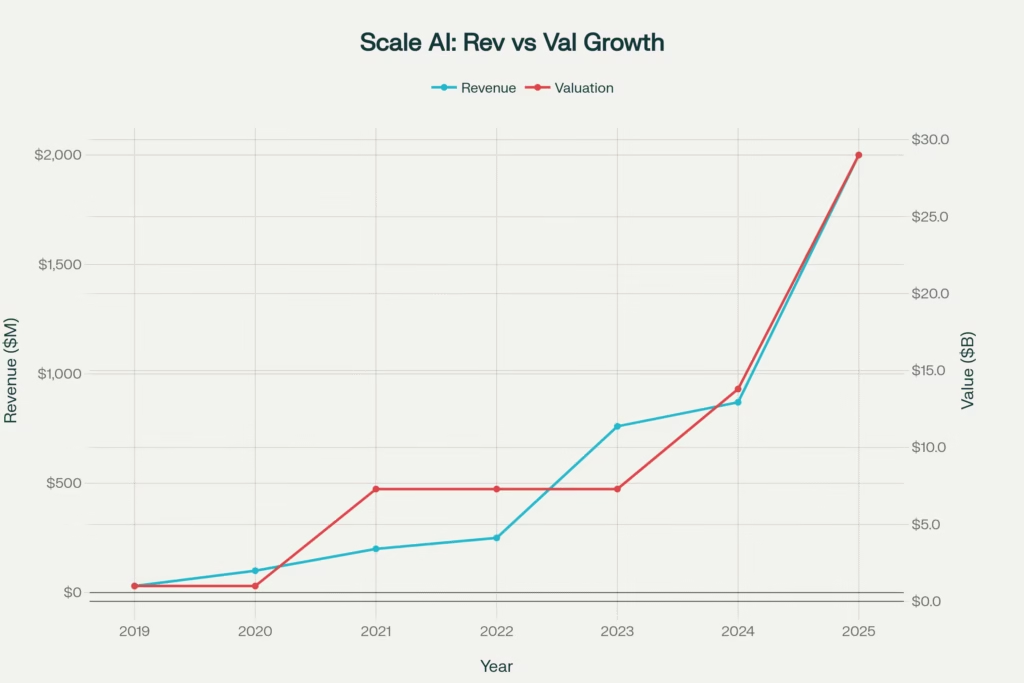
Scale AI’s explosive revenue and valuation growth from 2019-2025, culminating in Meta’s $14.3B investment
Scale AI’s Impact: Revolutionizing AI Across Industries
Scale AI’s influence extends far beyond its San Francisco headquarters to virtually every corner of the artificial intelligence ecosystem. The company’s data has powered breakthrough developments across multiple industries, establishing it as critical infrastructure for the AI revolution.
Generative AI: The Foundation of Modern Language Models
Scale’s partnership with OpenAI proved transformative for both companies. The collaboration began with early experiments in reinforcement learning with human feedback (RLHF) on GPT-2 and scaled to support InstructGPT and beyond. Scale’s human feedback systems reduced toxic outputs by 90% in early OpenAI models, demonstrating the crucial role of human-guided training in AI safety.
However, this relationship became complicated following Meta’s investment. OpenAI officially ended its partnership with Scale AI in June 2025, citing a desire to work with data providers that could match their innovation pace. While OpenAI maintained the decision was unrelated to the Meta deal, industry observers noted the timing suggested competitive concerns about Meta’s access to Scale’s services.
Autonomous Vehicles: Accelerating Self-Driving Technology
Scale’s Autonomy Data Engine has powered breakthroughs in Level 4 autonomous driving across the industry. The platform’s impact on GM Cruise exemplifies its value proposition: Scale reduced lidar annotation time by 60%, accelerating robotaxi deployment timelines and saving millions in development costs.
Toyota, Honda, and Waymo represent Scale’s marquee autonomous vehicle clients, each leveraging the platform’s ability to process massive volumes of sensor data with unprecedented precision. The company’s annotation capabilities extend beyond simple object detection to complex scenarios like construction zones, emergency vehicle detection, and adverse weather conditions edge cases that determine the difference between successful autonomous systems and catastrophic failures.
National Security AI: Powering America’s Defense Capabilities
Scale’s defense business represents both its most sensitive and potentially most lucrative market segment. The company has secured multiple contracts with the U.S. Department of Defense, including a flagship $250 million blanket purchasing agreement that gives all federal agencies access to Scale’s technology.
Project Thunderforge, announced in March 2025, represents Scale’s most ambitious defense initiative. This Department of Defense flagship program leverages AI agents for U.S. military planning and operations, working with partners including Anduril and Microsoft to develop advanced decision-making support systems. The program initially focuses on Indo-Pacific Command (INDOPACOM) and European Command (EUCOM) before expanding globally.
The defense business carries both strategic advantages and controversies. While government contracts provide stable revenue streams and validate Scale’s technology, they also attract scrutiny from critics concerned about AI’s military applications. Scale maintains that all defense work operates under human oversight, though this assurance hasn’t satisfied all stakeholders.
Scale AI Competitor Analysis
| Company | Founded | Valuation (2024-2025) | Revenue (Latest) | Primary Focus | Key Differentiator | Workforce Model | Major Clients |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Scale AI | 2016 | $29B | $870M (2024) | Full-stack AI data | Scale + defense contracts | Global contractors | Meta, OpenAI, DOD |
| Labelbox | 2018 | $2.1B | $50M est | Enterprise platform | Enterprise-first design | Mixed model | Fortune 500 |
| Appen | 1996 | $0.12B (Public) | $447M (2023) | Crowdsourcing | Established global network | Crowd + managed | Microsoft, Tesla |
| SuperAnnotate | 2018 | $0.5B | $25M est | Computer vision | Advanced CV tools | Hybrid approach | Mercedes, Snap |
| Surge AI | 2020 | $15B+ | $1B+ (2024) | Expert labeling | High-end expertise | Expert network | Google, OpenAI |
| iMerit | 2000 | Private | $250M+ | Global workforce | Cost efficiency | Managed teams | Microsoft, PayPal |
| Mighty AI (Uber) | 2014 | Acquired | N/A | Autonomous vehicles | Specialization | In-house + contractors | Uber (internal) |
| Amazon SageMaker | 2017 | N/A (AWS) | Part of AWS | Cloud ML platform | AWS integration | Automated + human | Amazon ecosystem |
Behind the Scenes: Global Workforce and Complicated Realities
Scale AI’s success story carries a darker undercurrent involving the exploitation of workers in developing nations who perform the company’s core data annotation tasks. Investigative reporting has revealed concerning patterns in Scale’s labor practices that highlight tensions between Silicon Valley profits and global workforce equity.
The Philippines: Ground Zero for AI Labor
In Cagayan de Oro, Philippines, Scale AI operates through its Remotasks subsidiary what investigators have characterized as “digital sweatshops”. Former employees report that at least 10,000 workers in this single city perform data annotation tasks for Scale, often earning between $2-$8 per hour for complex cognitive work.
Working conditions in Scale’s Philippines operations reveal the harsh realities behind AI’s data infrastructure. Workers crowd into windowless rooms with minimal supervision, working in three-shift systems covering 24-hour operations. The company initially offered above-minimum wages to attract workers, but compensation has steadily decreased as Scale expanded operations to lower-cost countries.
Labor Rights Investigations and Legal Challenges
The U.S. Department of Labor investigation into Scale AI, active from August 2024 through May 2025, examined potential violations of the Fair Labor Standards Act. The investigation focused on worker misclassification, unpaid wages, and illegal retaliation against employees. While the investigation was ultimately closed without findings, it highlighted ongoing concerns about Scale’s labor practices.
Multiple lawsuits filed between December 2024 and January 2025 alleged that Scale misclassified workers as contractors rather than employees, depriving them of benefits including overtime pay and sick leave. Scale has vigorously denied these allegations, maintaining that its compensation meets or exceeds local living wage standards.
The Race to the Bottom: Global Competition for Cheap Labor
Scale’s strategy of geographic arbitrage has created downward pressure on wages across multiple countries. Former employees report that Scale transferred annotation projects from the Philippines to Kenya, Nigeria, and Venezuela to access even cheaper labor. This “race to the bottom” approach maximizes Scale’s profit margins while minimizing compensation for the human intelligence that powers AI systems.
The ethical implications of this model extend beyond immediate worker welfare to broader questions about the sustainability of AI development. As Scale’s operations demonstrate, the “artificial” in artificial intelligence often depends heavily on human labor labor that remains largely invisible to end users and inadequately compensated relative to the value it creates.
Vision, Challenges, and the 2025 AI Landscape
Meta’s $14.3 Billion Gambit: Wang Joins the Superintelligence Race
The Meta investment announced in June 2025 represents far more than a traditional funding round it constitutes a strategic repositioning that could determine the future of artificial intelligence. Meta’s $14.3 billion investment for a 49% stake valued Scale at $29 billion, making it one of the largest AI deals in history.
Mark Zuckerberg’s personal recruitment of Wang reflects Meta’s urgent need to accelerate its AI capabilities. As Meta’s first-ever Chief AI Officer, Wang now leads the newly formed Meta Superintelligence Labs (MSL), tasked with developing AI systems that exceed human intelligence across all domains.
The MSL team reads like a who’s who of AI research talent, assembled through aggressive recruiting that included signing bonuses up to $100 million for individual researchers. Key additions include former OpenAI researchers, Google DeepMind scientists, and Anthropic executives, representing a significant brain drain from Meta’s competitors.
The Customer Exodus: Competitive Concerns Drive Client Departures
The Meta deal’s immediate aftermath revealed the competitive tensions underlying Scale’s business model. Google, Scale’s largest customer, immediately announced plans to sever ties with the company following the Meta investment. Google had spent approximately $150 million on Scale’s services in 2024 and was planning similar expenditures for 2025 before abruptly halting the relationship.
Microsoft and xAI also reportedly began exploring alternatives to Scale’s services, concerned that Meta’s ownership could provide insights into their AI development strategies. This customer flight directly contributed to Scale’s July 2025 workforce reduction, as the company struggled to replace lost revenue from major clients.
July 2025 Layoffs: Growing Pains Amid Strategic Transformation
Scale AI’s 14% workforce reduction in July 2025, affecting 200 full-time employees and 500 contractors, revealed the challenges accompanying its strategic transformation. Interim CEO Jason Droege cited “excessive bureaucracy” and overly rapid expansion in the generative AI division as primary factors necessitating the restructuring.
The layoffs concentrated heavily in Scale’s generative AI business unit, which Droege acknowledged had been unprofitable despite significant revenue growth. The restructuring consolidated 16 GenAI teams into five core groups, reflecting a more focused approach to business operations.
Market Landscape: Scale AI’s Position in the Expanding Data Economy
The artificial intelligence data labeling market represents one of the fastest-growing segments in the broader AI economy, with multiple research firms projecting explosive expansion through 2032. Scale AI’s dominant position in this market provides crucial context for understanding both its current success and future challenges.
Market Growth Projections: A $100+ Billion Opportunity
Research from leading market intelligence firms reveals the extraordinary growth potential in AI data services:
- Coherent Market Insights projects the market will grow from $4.87 billion in 2025 to $29.11 billion by 2032, representing a 29.1% CAGR
- Precedence Research offers an even more optimistic forecast, predicting growth from $22.46 billion in 2025 to $118.85 billion by 2034
- Grand View Research estimates more conservative but still substantial growth to $17.10 billion by 2030
These projections reflect the fundamental shift toward AI-powered applications across virtually every industry, from healthcare and finance to automotive and entertainment. Each new AI application requires massive amounts of precisely labeled training data, creating sustained demand for Scale’s services.
Competitive Landscape: Scale’s Advantages and Vulnerabilities
Scale AI operates in an increasingly crowded market populated by both established players and innovative newcomers. Key competitors include:
Labelbox focuses primarily on enterprise customers with sophisticated annotation software and managed services. The company has raised $189 million across five funding rounds and works with industry leaders including Google, Lyft, and Allstate.
Appen represents the incumbent leader with a global workforce of approximately one million contractors worldwide. As a publicly traded company, Appen offers greater transparency than Scale but has struggled with investor confidence amid competitive pressures.
Surge AI has emerged as a formidable competitor, reportedly generating over $1 billion in revenue in 2024 while seeking up to $1 billion in new funding at a $15+ billion valuation. The company, founded by former Google and Meta engineer Edwin Chen, has capitalized on Scale’s recent customer departures to expand its market position.
Scale AI Market Segments
| Market Segment | Scale AI Market Share | Total Market Size (2024) | Growth Rate (CAGR) | Key Competitors |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Autonomous Vehicles | 25% | $8.5B | 28% | Appen, Mighty AI |
| Generative AI/LLMs | 35% | $12.3B | 45% | Surge AI, Labelbox |
| Defense/Government | 40% | $3.2B | 22% | Palantir, Booz Allen |
| Healthcare AI | 15% | $15.1B | 31% | iMerit, Appen |
| Retail/E-commerce | 10% | $6.8B | 26% | Labelbox, SuperAnnotate |
| Computer Vision | 30% | $9.4B | 33% | SuperAnnotate, V7 |
| Natural Language Processing | 25% | $7.2B | 29% | Surge AI, Appen |
| Robotics/Manufacturing | 20% | $4.1B | 24% | iMerit, Mighty AI |
Scale’s competitive advantages include its end-to-end platform capabilities, defense contract portfolio, and data network effects. However, the Meta investment has complicated its positioning by creating concerns about competitive neutrality among potential clients.
Industry Challenges: Synthetic Data and Automation Threats
The emergence of synthetic data generation and automated labeling technologies poses long-term challenges to Scale’s business model. As AI systems become more sophisticated at generating realistic training data and performing self-annotation, the demand for human-powered data services may decline.
Leading AI companies including OpenAI, Google, and Anthropic are investing heavily in synthetic data capabilities to reduce dependence on external data providers. While current synthetic data technologies cannot fully replace human annotation for complex tasks, continued advancement could erode Scale’s market over time.
Regulatory pressures around AI development and data privacy also create uncertainty for Scale’s operations. The European Union’s AI Act and similar regulations worldwide may impose new requirements for data provenance and quality documentation that could advantage or disadvantage different market participants.
Financial Performance and Valuation Analysis
Scale AI’s financial trajectory from 2019 through 2025 illustrates both the explosive growth potential and inherent volatility of AI infrastructure businesses. The company’s revenue expansion from $30 million in 2019 to an expected $2 billion in 2025 represents a compound annual growth rate exceeding 100%.
Revenue Growth: The GenAI Boom’s Impact
The 2023 revenue surge from $250 million to $760 million directly correlates with the generative AI boom following ChatGPT’s release. Major AI companies including OpenAI, Anthropic, and Google dramatically increased their data labeling expenditures to improve model performance through reinforcement learning with human feedback.
2024 performance continued the growth trajectory with revenue reaching $870 million and an annualized run rate of $1.5 billion by year-end. Scale’s ability to more than triple revenue while maintaining gross margins above 50% demonstrated the scalability advantages of its platform approach.
2025 projections of $2 billion in revenue face significant uncertainty due to customer departures following the Meta deal. While Meta’s investment provides financial resources and strategic support, the loss of Google and potential departures by other major clients could impact near-term growth trajectories.
Scale AI Financial Timeline
| Year | Revenue ($M) | Valuation ($B) | Employees | Contractors | Revenue Multiple | Major Funding Round |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2019 | 30 | 1.0 | 150 | 5000 | 33.3 | Series C $100M |
| 2020 | 100 | 1.0 | 300 | 15000 | 10.0 | Growth funding |
| 2021 | 200 | 7.3 | 400 | 35000 | 36.5 | Series E $325M |
| 2022 | 250 | 7.3 | 600 | 70000 | 29.2 | Series E extension |
| 2023 | 760 | 7.3 | 750 | 90000 | 9.6 | Strong growth |
| 2024 | 870 | 13.8 | 900 | 120000 | 15.9 | Series F $1B |
| 2025 | 2000 | 29.0 | 900 | 100000 | 14.5 | Meta investment $14.3B |
Valuation Metrics: Premium Pricing for AI Infrastructure
Scale’s $29 billion valuation following the Meta investment represents approximately 14.5x projected 2025 revenue, a premium multiple that reflects both growth expectations and strategic value. This valuation positions Scale among the most valuable private companies globally and exceeds the market capitalizations of many established technology firms.
Comparative analysis with public market peers reveals Scale’s premium positioning. Traditional business process outsourcing companies typically trade at 2-4x revenue multiples, while high-growth SaaS companies command 10-15x revenue multiples. Scale’s valuation implies expectations of sustained high growth and expanding profit margins as the AI market matures.
Risk factors affecting valuation include customer concentration, regulatory scrutiny, competitive threats from automated solutions, and execution challenges in new market segments. The Meta investment mitigates financial risks but introduces new competitive dynamics that could impact long-term value creation.
The Global Implications: Scale AI and Geopolitical AI Competition
Wang’s evolution from startup founder to strategic national asset reflects the geopolitical dimensions of artificial intelligence competition. His warnings about China’s advancing AI capabilities and advocacy for domestic data and energy abundance position him as a key voice in technology policy discussions.
U.S.-China AI Competition: Data as Strategic Resource
Scale’s defense contracts and government relationships highlight artificial intelligence’s role in national security competition. The company’s work with INDOPACOM and EUCOM directly supports U.S. military planning in regions where China represents the primary strategic competitor.
Data sovereignty concerns have become central to AI policy as governments recognize the strategic importance of training data quality and provenance. Scale’s control over vast datasets used by American AI companies creates both opportunities and vulnerabilities in the broader context of technological competition.
Export Controls and Technology Transfer
The Meta investment structure as a minority stake rather than full acquisition may reflect considerations about export control regulations and technology transfer restrictions. Scale’s defense work requires maintaining security clearances and operational independence that could be compromised by foreign ownership or control.
International expansion remains challenging for Scale given the sensitive nature of its defense work and the classified datasets it processes. The company’s global workforce model creates additional complexities around data security and access controls for different client segments.
Lessons for Entrepreneurs, Investors, and Policymakers
Wang’s journey from MIT dropout to AI infrastructure mogul offers valuable insights for multiple stakeholder groups navigating the artificial intelligence revolution.
For Entrepreneurs: Platform Strategy and Market Timing
Wang’s success demonstrates the power of identifying infrastructure gaps in emerging technology markets. By focusing on data quality rather than flashier AI applications, Scale captured a defensive position that became more valuable as the market matured.
Platform effects enabled Scale to benefit from growth across multiple AI applications rather than betting on individual use cases. This diversification strategy provided resilience during market downturns and positioned the company to capture value from unexpected growth in generative AI.
Talent acquisition and retention proved crucial to Scale’s evolution, particularly as the company expanded from autonomous vehicles to generative AI and defense applications. Wang’s ability to attract domain experts and manage complex workforce operations became a core competitive advantage.
For Investors: Infrastructure Value in Technology Markets
The Scale AI investment thesis validates the “picks and shovels” approach to technology investing, where companies providing fundamental infrastructure often capture more value than flashier application developers. Scale’s success demonstrates how data infrastructure can generate sustainable competitive advantages and premium valuations.
Market timing played a crucial role in Scale’s success, with the company benefiting from multiple waves of AI adoption across autonomous vehicles, generative AI, and defense applications. Investors who recognized these secular trends early achieved exceptional returns.
Regulatory and competitive risks require careful analysis in technology infrastructure investments. Scale’s labor practice investigations and customer concentration risks highlight the importance of due diligence around operational practices and market dependencies.
For Policymakers: Balancing Innovation with Worker Protection
Scale’s global workforce model illustrates the tensions between technological innovation and labor equity. Policymakers must address the economic disparities inherent in current AI development models while preserving incentives for continued innovation.
National security considerations around AI infrastructure require new frameworks for evaluating foreign investment and technology transfer. Scale’s defense work and Chinese-American leadership highlight the complexities of maintaining technological competitiveness while addressing security concerns.
International cooperation on AI governance could help address the “race to the bottom” dynamics in global data labeling markets while preserving innovation incentives for companies like Scale.
Takeaways: Critical Insights for the AI Era
1. Infrastructure Trumps Applications in Technology Markets
Scale’s success validates the principle that companies controlling fundamental infrastructure often capture more value than those building specific applications. Wang’s focus on data quality rather than end-user AI applications enabled Scale to benefit from growth across multiple market segments.
2. Global Workforce Models Require Ethical Frameworks
Scale’s labor controversies demonstrate that global arbitrage strategies must be balanced with fair compensation and working conditions. Companies pursuing similar models must develop sustainable approaches to international workforce management that address both efficiency and equity concerns.
3. Geopolitical Considerations Shape Technology Strategy
The Meta investment and defense contracts highlight how geopolitical competition increasingly influences business strategy in critical technology sectors. Entrepreneurs and investors must consider national security implications alongside traditional business metrics.
4. Customer Concentration Creates Strategic Vulnerabilities
Scale’s challenges following the Meta deal illustrate how customer concentration can create strategic vulnerabilities even for successful companies. Diversification across client segments and geographies remains crucial for long-term sustainability.
5. Regulatory Compliance Requires Proactive Management
Scale’s labor investigations and regulatory scrutiny demonstrate the importance of proactive compliance programs in technology companies with global operations. Early attention to regulatory requirements can prevent significant future liabilities.
Conclusion: The Future of Human-AI Collaboration
Alexandr Wang’s transformation from MIT dropout to AI mogul embodies the profound changes reshaping technology, labor, and geopolitical competition in the artificial intelligence era. His journey illustrates both the extraordinary opportunities and complex challenges inherent in building infrastructure for humanity’s most powerful technologies.
Scale AI’s evolution from Y Combinator startup to $29 billion Meta subsidiary reflects the fundamental importance of high-quality data in artificial intelligence development. Wang’s prescient recognition that “data is the new code” positioned Scale at the center of every major AI breakthrough over the past decade, from autonomous vehicles to large language models to military planning systems.
Yet Scale’s success story also reveals the human costs and ethical complexities underlying AI development. The company’s reliance on low-wage workers in developing nations, labor practice investigations, and regulatory scrutiny highlight tensions between technological progress and social equity that remain unresolved across the AI industry.
The Meta investment and Wang’s new role as Chief AI Officer mark a pivotal moment not just for Scale but for the broader artificial intelligence ecosystem. His leadership of Meta Superintelligence Labs positions him to influence the development of AI systems that could transform every aspect of human society. The success or failure of this endeavor will have implications far beyond financial returns for Meta shareholders.
Looking ahead, Wang faces challenges that extend well beyond business strategy to fundamental questions about the future of human-AI collaboration. How can AI development models ensure fair compensation for the human intelligence that powers artificial intelligence? How should democratic societies balance innovation incentives with worker protection and algorithmic accountability? How can America maintain technological leadership while addressing legitimate concerns about AI’s societal impact?
Wang’s journey from teenage programmer to AI infrastructure mogul demonstrates that individual vision and execution can reshape entire industries. As he leads Meta’s quest for artificial superintelligence, the decisions he makes will influence not just his company’s future but the trajectory of artificial intelligence development globally.
The data may be the new code, but Wang’s story reminds us that behind every AI breakthrough lies human intelligence, creativity, and ambition. The future of artificial intelligence will be determined not just by algorithms and compute power, but by the wisdom and values of the humans who guide its development.
What role do you think human judgment should play as AI systems become increasingly sophisticated? How can we ensure that the benefits of artificial intelligence are shared equitably across society? The comment section awaits your perspectives on these critical questions shaping our technological future.
2025 revenue and valuation figures marked with asterisks are projections subject to change based on market conditions and company performance.
References & Authoritative Sources
- Who is Alexandr Wang? – Comprehensive biographical info, early life, and career highlights. Alexandr Wang – Wikipedia
- The Birth of Scale AI: A Startup Story – Detailed company history, mission, and milestones. Scale AI – About Us Page
- What is Scale AI and How Does It Work? – Case study on platform use in media and data labeling operations. TIME x Scale AI – Customer Case Study
- Scale AI’s Impact: Revolutionizing AI Across Industries – News and analysis of Meta’s investment, partnerships, and valuation.
- Behind the Scenes: Global Workforce and Complicated Realities – Investigative insights into labor practices and annotation workforce. Digital Information World – Alexander Wang Story
- Vision, Challenges, and the 2025 AI Landscape – Wang’s direct perspectives on AI’s future and Meta engagement. Alexandr Wang Substack Interview
- General Context and Competitive Landscape – Latest updates on Scale AI’s offerings and market position. Scale AI – Wikipedia
- Additional Resources
Keywords: Alexandr Wang, Scale AI, AI startup, AI data labeling, generative AI startup, Y Combinator success stories, AI ethics, remote crowd work, national security AI, Scale AI valuation 2025, AI workforce, data annotation, human-in-the-loop AI, autonomous vehicles AI, AI defense contracts, Meta AI investment, artificial intelligence infrastructure, AI platform, RLHF (Reinforcement Learning with Human Feedback), AI synthetic data challenges, AI gig economy
Disclaimer: Transparency is important to us! This blog post was generated with the help of an AI writing tool. Our team has carefully reviewed and fact-checked the content to ensure it meets our standards for accuracy and helpfulness. We believe in the power of AI to enhance content creation, but human oversight is essential.




I do accept as true with all of the ideas you’ve introduced to your post. They’re very convincing and can certainly work. Nonetheless, the posts are too short for novices. May just you please lengthen them a little from next time? Thanks for the post.