The Ultimate Guide to Multi-Agent AI Workflow Frameworks
Picture this: It’s Monday morning, and Sarah, a marketing director at a growing SaaS company, stares at her computer screen with mounting frustration. Her team needs to coordinate content creation, social media scheduling, lead qualification, customer onboarding, and performance analytics all while ensuring nothing falls through the cracks. Like thousands of business leaders in 2025, Sarah faces the challenge of orchestrating complex AI workflows that span multiple tools, platforms, and processes.
This is where multi-agent AI workflow frameworks come to the rescue. In 2025, the AI agents market has exploded to $7.92 billion and is projected to reach $52.20 billion by 2030, growing at an astounding 45.82% CAGR. This isn’t just hype 85% of enterprises are planning to adopt AI agents into their business operations this year, with 92% of companies planning to increase their AI investments over the next three years.
The infographic above showcases six leading frameworks that are transforming how businesses automate their workflows: LangGraph, LangChain, AutoGen, CrewAI, Make.com, and n8n. Each offers unique strengths for different use cases, from complex stateful workflows to simple drag-and-drop automation. This comprehensive guide will help you navigate these options and choose the perfect framework for your specific needs.
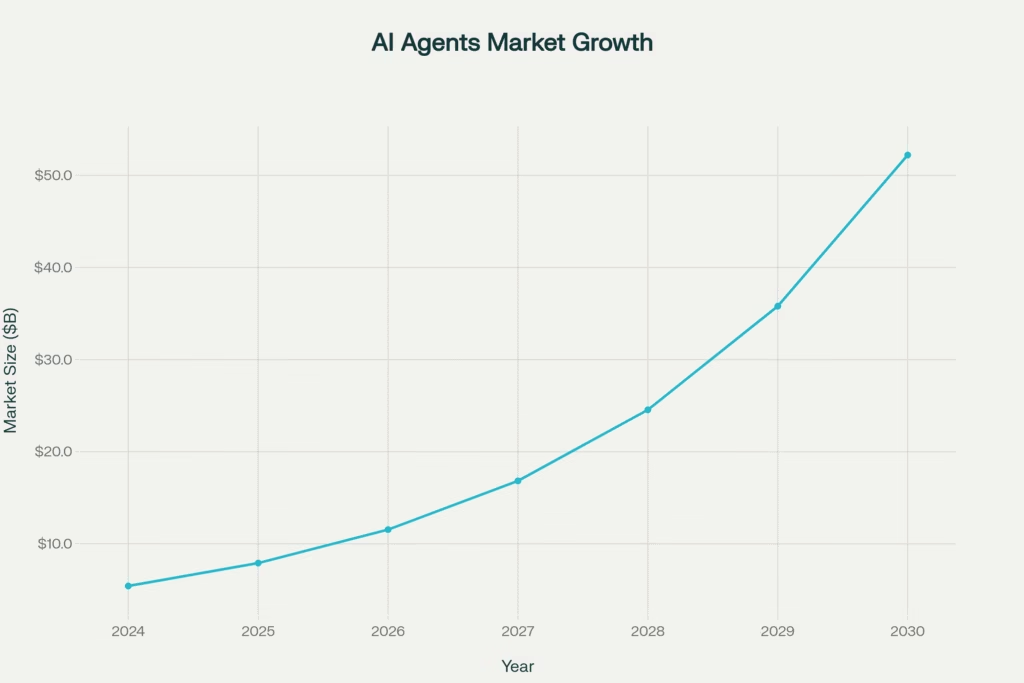
AI Agents Market Growth Projection 2024-2030 (CAGR: 45.82%)
What Are Multi-Agent AI Workflow Frameworks and Why Do They Matter?
Multi-agent AI workflow frameworks are sophisticated systems that orchestrate multiple specialized AI agents to work together autonomously, much like a well-coordinated team where each member has specific expertise and responsibilities. Instead of relying on a single AI to handle complex tasks, these frameworks break down intricate processes into manageable components, with each agent contributing domain-specific knowledge and capabilities.
Think of it as the difference between asking one person to plan your entire wedding versus assembling a team of specialists—a venue coordinator, catering expert, photographer, and florist—who collaborate seamlessly to create your perfect day. Multi-agent systems overcome the limitations of single-agent approaches by enabling parallel processing, specialized expertise, and intelligent coordination.
The business impact is undeniable. Companies implementing multi-agent systems report 72% operational efficiency gains, 69% elevated precision, and 65% better decision-making. For instance, Klarna uses LangGraph to handle customer support for 85 million users, cutting resolution time by 80%, while Uber automates code migrations with networks of agents, and Elastic orchestrates AI agents for threat detection.
Why Multi-Agent Frameworks Matter in 2025:
- Scale Beyond Human Capacity: Agents can process thousands of tasks simultaneously
- Specialized Expertise: Each agent focuses on what it does best, improving accuracy
- 24/7 Operation: Continuous workflow execution without human intervention
- Cost Reduction: 52% of organizations report significant cost reductions from agent implementation
- Future-Proofing: By 2028, 68% of customer interactions are expected to be handled by autonomous tools
Side-by-side Comparison: LangGraph, LangChain, AutoGen, CrewAI, Make.com, and n8n
Understanding the nuances between these frameworks is crucial for making the right choice. Let’s break down each platform’s core strengths, ideal use cases, and technical requirements.
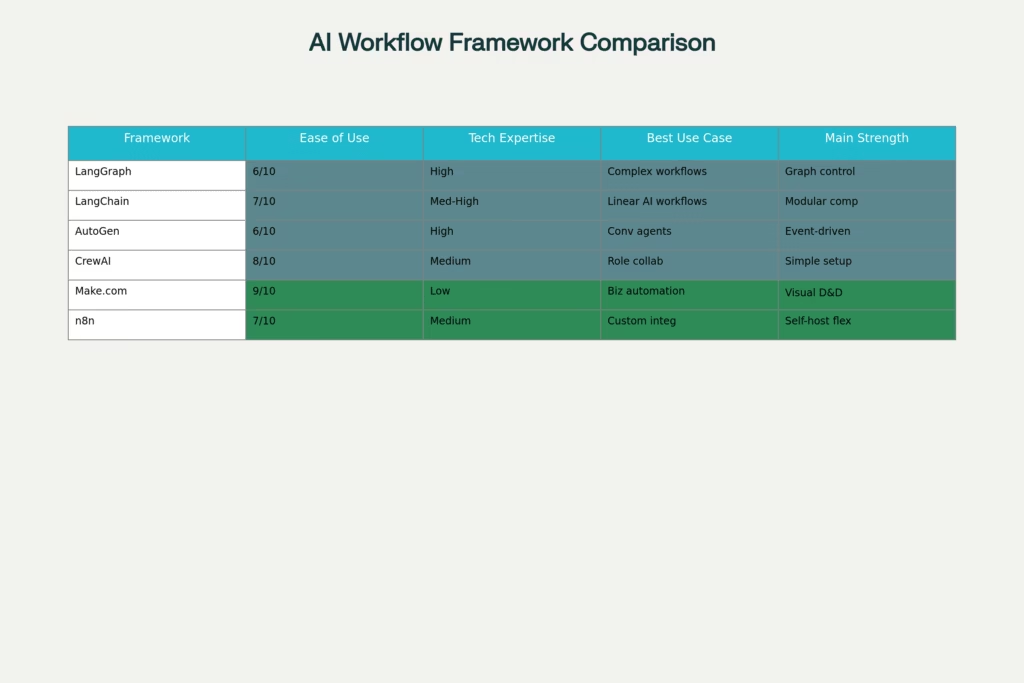
Comprehensive Feature Comparison Matrix for AI Workflow Automation Frameworks
LangGraph: The Graph-Based Orchestrator
LangGraph represents the cutting edge of stateful, multi-agent workflow design. Built by the LangChain team, it treats agent workflows as directed acyclic graphs (DAGs) where each node represents an operation and edges define control flow. This architecture provides unprecedented control over complex, multi-step interactions that would be challenging to manage through simple conversational approaches.
Key Strengths:
- Stateful Memory Management: Maintains context across long-running workflows
- Human-in-the-Loop: Built-in approval gates and intervention points
- Streaming Support: Real-time updates on agent actions and reasoning
- Flexible Architecture: Supports single-agent, multi-agent, and hierarchical workflows
Best For: Enterprise applications requiring complex decision trees, regulatory compliance workflows, and scenarios demanding precise control over agent interactions.
Learning Curve: High—requires understanding of graph theory and state management principles.
LangChain: The Modular Foundation
LangChain pioneered the modular approach to LLM application development with its chain-based architecture. It excels at linear, sequential workflows where tasks flow predictably from one step to the next. While simpler than LangGraph, it provides the building blocks for rapid prototyping and straightforward AI applications.
Key Strengths:
- Extensive Ecosystem: Massive library of pre-built components and integrations
- RAG Workflows: Exceptional for retrieval-augmented generation applications
- Quick Prototyping: Fast setup for proof-of-concept projects
- Community Support: Largest developer community in the AI agent space
Best For: Content creation pipelines, document processing, simple chatbots, and rapid prototyping.
Learning Curve: Medium-High requires familiarity with Python and LLM concepts.
AutoGen: The Conversational Coordinator
Microsoft’s AutoGen takes a unique approach by framing multi-agent interaction as conversational collaboration. The recently released AutoGen v0.4 introduced a complete architectural overhaul with asynchronous, event-driven design that scales to enterprise requirements.
Key Strengths:
- Event-Driven Architecture: Asynchronous messaging enables parallel agent operations
- Enterprise Integration: Deep integration with Microsoft’s ecosystem and Semantic Kernel
- Observability: Built-in tracking, tracing, and debugging capabilities
- AutoGen Studio: No-code interface for rapid workflow prototyping
Best For: Enterprise environments, Microsoft-centric infrastructure, research applications, and scenarios requiring complex agent conversations.
Learning Curve: High—steep initial setup but powerful once mastered.
CrewAI: The Orchestrated Team
CrewAI stands out with its role-based architecture that mimics human organizational structures. Each agent is assigned specific roles, expertise areas, and responsibilities, making it intuitive for business users to understand and implement.
Key Strengths:
- Role-Based Design: Natural mapping to business team structures
- Fast Deployment: Minimal code required for complex workflows
- Independent Framework: Built from scratch, not dependent on other agent frameworks
- Performance: 5.76x faster execution compared to some alternatives in certain tasks
Best For: Marketing automation, customer service, content creation teams, and businesses wanting quick deployment.
Learning Curve: Medium—business-friendly concepts with technical flexibility.
Make.com: The Visual Automation Powerhouse
Make.com (formerly Integromat) represents the pinnacle of no-code automation. With its signature drag-and-drop visual interface, it makes sophisticated workflow automation accessible to non-technical users.
Key Strengths:
- Visual Interface: Intuitive scenario-based workflow builder
- Extensive Integrations: Over 2,400 pre-built app connections
- Enterprise Ready: SOC2 compliance, SSO, and 24/7 support
- Speed: 5-10x faster automation development compared to custom coding
Best For: Business process automation, marketing workflows, data synchronization, and teams without technical expertise.
Learning Curve: Low—designed for immediate productivity.
n8n: The Self-Hosted Specialist
n8n (pronounced “nodemation”) offers the unique combination of visual workflow building with self-hosting capabilities. Its open-source nature and JavaScript/Python code integration make it a favorite among developers who want control without complexity.
Key Strengths:
- Self-Hosting: Complete control over data and infrastructure
- Code Integration: Native JavaScript and Python support for custom logic
- Open Source: Fair-code license with community-driven development
- Cost Effective: Self-hosting option eliminates per-operation fees
Best For: Developer teams, organizations with strict data privacy requirements, and businesses wanting cost-effective scaling.
Learning Curve: Medium—technical setup required but user-friendly interface.
How Do These Frameworks Work? [Step-by-Step Workflows Explained]
Understanding how each framework approaches workflow orchestration helps clarify which solution fits your specific needs.
Code-Heavy Frameworks: The Technical Powerhouses
LangGraph Workflow Example:
- Define State Schema: Create data structures to maintain context
- Design Graph Nodes: Each node represents an agent or operation
- Configure Edges: Define conditional transitions between nodes
- Implement Memory: Set up checkpointers for persistence
- Deploy with Monitoring: Use LangSmith for observability
AutoGen Process Flow:
- Initialize Agent Roles: Define specialized agents with distinct capabilities
- Set Conversation Patterns: Configure how agents communicate
- Enable Event Triggers: Set up asynchronous message handling
- Implement Human Oversight: Add approval gates where needed
- Monitor Execution: Track performance through built-in telemetry
No-Code/Low-Code Solutions: The Accessibility Champions
Make.com Scenario Building:
- Choose Triggers: Select what starts your automation
- Add Modules: Drag and drop app actions into your workflow
- Configure Logic: Set conditions and filters visually
- Test Integration: Run scenarios to verify functionality
- Deploy and Monitor: Activate with real-time execution tracking
n8n Node Configuration:
- Set Trigger Node: Define workflow starting conditions
- Connect Action Nodes: Chain operations using visual connections
- Add Custom Logic: Insert JavaScript/Python code where needed
- Configure Webhooks: Enable real-time data flow
- Deploy Self-Hosted: Install on your infrastructure or use cloud
Use Cases: When to Use LangGraph vs LangChain vs AutoGen vs CrewAI
Choosing the right framework depends heavily on your specific use case, technical requirements, and organizational constraints.
Enterprise Process Automation
- LangGraph: Complex compliance workflows with multiple approval stages
- AutoGen: Cross-departmental coordination requiring human oversight
- Make.com: Employee onboarding, contract management, incident response
- n8n: Custom integrations with existing enterprise systems
Customer Service and Support
- CrewAI: Role-based support teams (L1, L2, specialist agents)
- LangChain: Simple chatbots with knowledge base integration
- Make.com: Ticket routing, SLA tracking, automated responses
- AutoGen: Complex issue resolution requiring multiple specialists
Marketing and Content Creation
- CrewAI: Content teams with researchers, writers, and editors
- LangGraph: Multi-step content approval and distribution workflows
- Make.com: Social media scheduling, lead nurturing campaigns
- n8n: Custom analytics and reporting pipelines
Financial Services and Compliance
- LangGraph: Regulatory compliance with audit trails
- AutoGen: Loan processing with multiple validation steps
- Make.com: Invoice processing, payment automation
- n8n: Custom financial data integration and reporting
No-Code vs Low-Code: Make.com and n8n for Non-Developers
The distinction between no-code and low-code approaches is crucial for teams evaluating their technical capabilities and long-term scalability needs.
No-Code Advantages (Make.com)
Make.com exemplifies the no-code philosophy: empowering non-technical users to create sophisticated automations without writing a single line of code. This approach offers several compelling advantages:
- Immediate Productivity: Users can create workflows on day one without training
- Visual Clarity: See exactly how data flows through your automation
- Maintenance Simplicity: Updates don’t require developer intervention
- Lower Total Cost: No need for specialized development resources
When No-Code Works Best:
- Standard business processes with predictable patterns
- Teams without technical expertise
- Rapid prototyping and iteration needs
- Budget constraints limiting developer hiring
Low-Code Benefits (n8n)
n8n represents the low-code approach: providing visual tools while maintaining the flexibility to add custom code when needed. This hybrid model offers unique advantages:
- Unlimited Customization: JavaScript and Python integration for complex logic
- Cost Scalability: Self-hosting eliminates per-operation fees
- Data Control: Complete ownership of sensitive information
- Future-Proofing: Ability to extend functionality as needs evolve
When Low-Code Excels:
- Organizations with some technical expertise
- Complex integration requirements
- Strict data privacy or compliance needs
- Long-term scalability concerns
Best Practices for Choosing the Right AI Orchestration Framework
Selecting the optimal framework requires careful evaluation of multiple factors beyond just features and pricing.
Technical Assessment Framework
1. Evaluate Your Team’s Capabilities
- High Technical Expertise: Consider LangGraph, AutoGen for maximum flexibility
- Medium Technical Skills: CrewAI or n8n provide good balance
- Non-Technical Teams: Make.com offers immediate productivity
2. Define Your Use Case Complexity
- Simple Linear Workflows: LangChain, Make.com excel here
- Complex Multi-Agent Coordination: LangGraph, AutoGen designed for this
- Role-Based Collaboration: CrewAI’s sweet spot
3. Consider Infrastructure Requirements
- Cloud-First: Make.com, CrewAI cloud offerings
- Hybrid Deployment: LangGraph with LangChain ecosystem
- Self-Hosted Control: n8n’s primary advantage
Strategic Decision Matrix
Choose LangGraph When:
- Building enterprise-grade applications with complex state management
- Requiring human-in-the-loop workflows with approval gates
- Need streaming capabilities for real-time user feedback
- Working with LangChain ecosystem components
Choose AutoGen When:
- Operating in Microsoft-centric environments
- Building conversational agent networks
- Requiring enterprise observability and compliance
- Need asynchronous, event-driven architectures
Choose CrewAI When:
- Mapping workflows to existing team structures
- Prioritizing speed of implementation over customization
- Building customer service or marketing automation
- Want framework independence from other platforms
Choose Make.com When:
- Non-technical team members need to build workflows
- Require extensive third-party app integrations
- Want enterprise-ready features out of the box
- Budget allows for per-operation pricing model
Choose n8n When:
- Self-hosting is required for data privacy
- Team has technical skills for custom development
- Cost scaling is a long-term concern
- Need hybrid visual/code approach for flexibility
Expert Tips: Optimizing Multi-Agent AI Automation for Business
Implementing multi-agent systems successfully requires more than just choosing the right framework—it demands strategic thinking about workflows, team capabilities, and long-term scalability.
Implementation Best Practices
Start Small, Scale Smart
Begin with a single, well-defined process rather than attempting to automate everything at once. 72% of successful implementations start with pilot projects that demonstrate clear ROI before expanding. Choose workflows with:
- Clear inputs and outputs
- Minimal exceptions requiring human judgment
- Measurable success metrics
- Stakeholder buy-in across departments
Design for Exceptions
Real-world processes rarely follow happy-path scenarios. Build fallback flows and escalation procedures into every workflow. Companies report that 90% of automation failures stem from inadequate exception handling rather than technical limitations.
Implement Monitoring from Day One
63% of organizations plan to increase their AI investments by 2026, but only those with proper observability see sustained success. Establish dashboards tracking:
- Task completion rates and processing times
- Error frequency and resolution paths
- Cost savings and efficiency gains
- User adoption and satisfaction metrics
Organizational Change Management
Build Cross-Functional Teams
Successful multi-agent implementations require collaboration between business stakeholders, IT teams, and end users. 87% of executives say seamless integration with existing tools is critical for success.
Invest in Training and Documentation
Even no-code platforms require user education. Companies with comprehensive training programs see 55% higher adoption rates compared to those relying solely on self-service learning.
Plan for Governance and Compliance
As 68% of customer interactions move to autonomous systems by 2028, establishing clear governance frameworks becomes essential. Define:
- Data handling and privacy protocols
- Approval workflows for sensitive operations
- Audit trails and regulatory compliance measures
- Security standards and access controls
Frequently Asked Questions about Multi-Agent AI Frameworks
How does LangChain differ from LangGraph?
LangChain focuses on linear, chain-based workflows ideal for sequential tasks like RAG pipelines and simple chatbots. LangGraph extends this with graph-based architecture supporting complex, stateful workflows with loops, conditional branching, and multi-agent coordination.
Is Make.com suitable for technical users?
While Make.com is designed for non-technical users, it offers significant value for technical teams through its 2,400+ integrations, enterprise features, and rapid deployment capabilities. Technical users appreciate the speed of implementation without sacrificing functionality.
Which AI orchestration tool integrates best with Salesforce?
Make.com provides the most comprehensive Salesforce integration with native connectors covering all major functions. n8n offers flexible custom integration through APIs, while code-heavy frameworks like LangGraph and AutoGen require more development effort for Salesforce connectivity.
Can multiple frameworks be used together?
Yes, hybrid approaches are common in enterprise environments. For example, organizations might use Make.com for standard business processes while deploying LangGraph for complex decision workflows, or use n8n for data integration with CrewAI for agent orchestration.
What’s the learning curve for each framework?
Make.com: Immediate productivity for non-technical users
CrewAI: 1-2 weeks for business users with basic technical skills
n8n: 2-4 weeks including self-hosting setup
LangChain: 4-6 weeks for developers new to LLM frameworks
AutoGen: 6-8 weeks including enterprise integration
LangGraph: 8-12 weeks for complex stateful applications
How do pricing models compare across frameworks?
Open Source: n8n (self-hosted), AutoGen, LangGraph core components
Per-Operation: Make.com charges per action, n8n cloud per workflow execution
Subscription: CrewAI cloud offerings, enterprise versions of all frameworks
Usage-Based: LangChain/LangGraph through LangSmith for monitoring and hosting
What are the security implications of each approach?
Highest Security Control: n8n self-hosted, AutoGen enterprise deployment
Enterprise Security: Make.com SOC2 compliance, CrewAI cloud security
Flexible Security: LangGraph/LangChain allow custom security implementations
Data Residency: Critical for regulated industries, favoring self-hosted solutions
How do these frameworks handle AI model changes?
Model Agnostic: n8n, Make.com work with any API-accessible model
LLM Optimized: CrewAI, AutoGen designed specifically for language models
Ecosystem Dependent: LangGraph/LangChain tightly integrated with their model providers
Vendor Lock-in: Consider long-term implications of framework-specific model integrations
Conclusion: Navigating the Multi-Agent Future
As we’ve explored throughout this comprehensive guide, the age of multi-agent AI systems has arrived, with the market exploding from $5.43 billion in 2024 to a projected $52.20 billion by 2030. The six frameworks we’ve examined—LangGraph, LangChain, AutoGen, CrewAI, Make.com, and n8n—each offer unique approaches to solving the complex challenge of AI workflow orchestration.
The choice ultimately depends on your specific needs:
- For maximum control and complex stateful workflows: LangGraph provides unparalleled flexibility
- For rapid prototyping and linear processes: LangChain remains the go-to choice
- For enterprise conversational agents: AutoGen’s Microsoft integration excels
- For intuitive role-based collaboration: CrewAI offers the fastest path to deployment
- For non-technical teams needing powerful automation: Make.com delivers immediate productivity
- For developers wanting self-hosted flexibility: n8n provides the perfect balance
The future belongs to organizations that can effectively orchestrate AI agents to handle complex, multi-step workflows while maintaining human oversight where it matters most. Whether you’re Sarah from our opening story looking to streamline marketing operations, or an enterprise architect designing compliance workflows, the right framework choice can transform your organization’s capabilities.
Take action today: Start with a pilot project using the framework that best matches your team’s capabilities and business requirements. The 92% of companies increasing AI investments aren’t waiting and neither should you.
What framework are you considering for your multi-agent AI implementation? Share your thoughts and questions in the comments below, and don’t forget to subscribe for more insights on AI automation trends and best practices.
Keywords: multi-agent AI frameworks, AI workflow automation, LangGraph, LangChain, AutoGen, CrewAI, Make.com, n8n, agent orchestration, LLM automation, generative AI pipelines, workflow builder, no-code AI tools, low-code automation, AI integration, conversational AI, business process automation, semantic SEO, autonomous AI agents, enterprise AI, AI agents for business, AI automation trends 2025, AI-powered workflows, stateful AI workflows, open source AI frameworks, operational efficiency, AI orchestration, workflow management, digital transformation, AI agent comparison, AI for enterprises
Disclaimer: Transparency is important to us! This blog post was generated with the help of an AI writing tool. Our team has carefully reviewed and fact-checked the content to ensure it meets our standards for accuracy and helpfulness. We believe in the power of AI to enhance content creation, but human oversight is essential.





I believe this web site contains some very excellent information for everyone : D.
Thank you so much for your kind words! It’s wonderful to hear that you found this site and enjoyed the information. Your feedback is genuinely appreciated and encourages me to continue creating valuable content. Looking forward to seeing you around more often!
AI Tech Quest Team